By David Horky
The Gabriel Dumont Institute (GDI) maintains a list of over 5,000 individuals whose names are engraved on the National Métis Veterans’ Memorial Monument in Batoche, Saskatchewan. Unveiled in 2014, the monument serves to recognize, remember and honour veterans from across the Métis Nation Homeland who have served Canada throughout history. The list of Métis veterans (PDF) provides the veteran’s name, service number, enlistment (the war or activity), and the location of their inscription on the monument (by column and row).
The GDI list has been invaluable for my own personal research about one of my distant relatives who fought and died in the First World War. I recently discovered Métis branches on my own family tree on the Métis Genealogy section of the Library and Archives Canada (LAC) website, and it was while doing this research that I found the digitized military service file of a distant relative, Private Arthur Carriere.
Searching the GDI list, I was proud to find an entry for a Private Arthur Carriere, confirming that he was indeed among the many names engraved on the National Métis Veterans’ Memorial Monument. I realized in the process that the service number on the GDI list—2293697—corresponded to the regimental number referring to the same soldier on the LAC website. This simple example demonstrates the great value of the GDI list to relatives and researchers interested in identifying Métis veterans from the 600,000 digitized service files in the Personnel Records of the First World War database.
Being able to access a digital copy of Arthur’s First World War service file—a tangible record of his involvement in the war—was a very personal way for me to pay my respects to one of my kin in remembrance of his service and sacrifice to our country. Despite the brevity of much of the information recorded on the various forms and documents in the file, they collectively provide a story, impressionistic to be sure, about Arthur’s brief and tragic wartime experience.
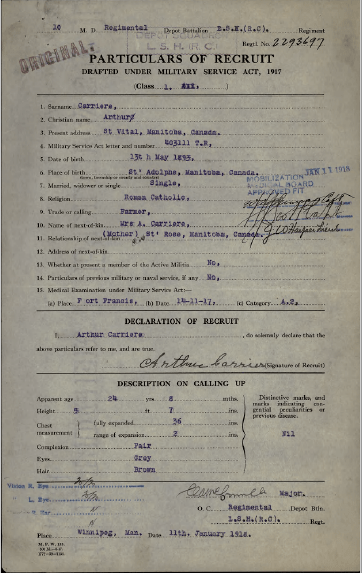
The Attestation Paper from Arthur Carriere’s digitized service file. (Library and Archives Canada, CEF 2293697)
Although there weren’t any explicit references to Arthur’s Métis heritage recorded in the file, I thought I could detect traces or clues in some of the records, especially the Attestation Paper, which provides basic information about his background at the time of his enlistment—age, occupation, residence, name and address of next of kin, etc. Born in 1893 in St. Adolphe, Manitoba, Arthur was 24 years old, single, and a farmer living in St. Vital, Manitoba at the time of his enlistment. His next of kin is his mother, A. (Angèle) Carriere, of Ste. Rose, Manitoba. The communities in particular struck my attention—all are Franco-Manitoban with strong and continuing Métis roots. The next of kin information is often very useful to trace Métis roots, as ethnic origin is not usually stated in the file.
The Attestation Paper also indicates the circumstances of Arthur’s enlistment—the most obvious being that he did not volunteer, but was drafted under the provisions of the Military Service Act. He reported for medical examination on November 14, 1917 in Fort Frances, Ontario, and was called up on January 11, 1918 in Winnipeg for active service as a private with the Lord Strathcona Horse (Royal Canadians), a regiment of mounted rifles.

The casualty form from Arthur Carriere’s digitized service file. (Library and Archives Canada, CEF 2293697)
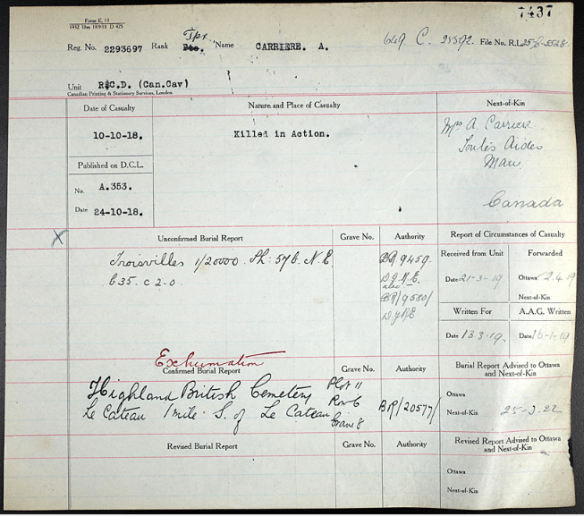
The Casualty Form—Active Service record provides us with a very brief outline of Arthur’s activities following his enlistment. Leaving Halifax on April 15, 1918 on the S.S. Melita, the Lord Strathcona Horse (Royal Canadians) arrived in Liverpool, England on April 28, 1918. On August 20, 1918, shortly after arriving in France), Arthur joined the Canadian Corps Reinforcement Centre where troops were held before being sent to reinforce existing units. A couple of weeks later on September 13, 1918, he was transferred to the Royal Canadian Dragoons (RCD), a regiment assigned to the Canadian Cavalry Brigade but that mainly played an infantry role throughout the war. Less than a month after joining the RCD, Arthur’s life was tragically cut short. On October 10, 1918, he is simply reported as “killed in action.” This is one month and a day short of the signing of the Armistice on November 11, 1918 that ended the First World War.

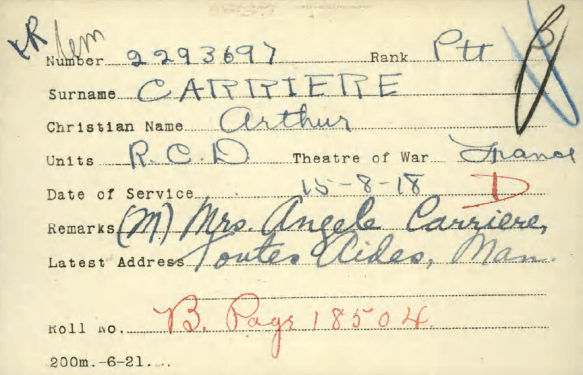
The entry for Arthur Carriere in the Circumstances of Death Registers, First World War.
A few more details about Arthur’s death is provided by another military record, the Circumstances of Death Registers, First World War, which the Canadian Expeditionary Forces (CEF) used to report the cause of a soldier’s death, where and when it occurred, and the soldier’s final resting place. The entry for Private Arthur Carriere indicates that on October 10, 1918 “while acting as a medical orderly at Brigade Headquarters in Troisvilles, he was killed by an enemy shell.” The location of his final resting place is given as Grave 8, Plot 11, Row C in the Highland British Cemetery, recorded in the Commonwealth War Graves Commission Register as being one mile south of Le Coteau, France.
Too many to list here, there are other First World War records held at LAC, as well as external sources of information that can provide valuable additional details about WWI soldiers and the various CEF units serving overseas in France and Flanders.
The medal card from Arthur Carriere’s digitized service file. (Library and Archives Canada, CEF 2293697)

The Memorial Cross card from Arthur Carriere’s digitized service file. (Library and Archives Canada, CEF 2293697)
Arthur’s story does not end simply with his death. The medals he garnered, such as the British War Medal and the Victory Medal, indicated by crossed-out capital letters “B” and “V” on the medal card along with the Memorial Cross, Scroll and Plaque, were dutifully given by a grateful nation to his mother in mourning.
The Franco-Manitoban Métis community of St. Norbert also felt the loss of Arthur’s death. Shortly after the end of war, they erected the St. Norbert War Memorial in recognition of the ultimate sacrifice paid by Arthur and 12 other local residents.
In this light, one can see in Arthur’s story a tradition of recognition and remembrance of the services rendered to Canada by veterans of Métis Nation communities that stretches back from the memorial erected in St. Norbert at the end of the Great War all the way to the present-day National Métis Veterans’ Memorial Monument in Batoche. The GDI acknowledges that there are probably many unknown Métis veterans who deserve our recognition and remembrance. Using the GDI form, you can submit the names and military service information of additional Métis veterans to engrave on the National Métis Veterans Historic Monument and ensure that they receive the recognition and honour due them from Canada and the Métis Nation.
David Horky is a senior archivist at Library and Archives Canada, Winnipeg office.

![On the left of the graphic, Tatânga Mânî [Chief Walking Buffalo] [George McLean] in traditional regalia on horse. In the middle, Iggi and girl engaging in a “kunik”, a traditional greeting in Inuit culture. On the right, Maxime Marion, a Métis guide stands holding a rifle. In the background, there is a map of Upper and Lower Canada, and text from the Red River Settlement collection.](https://thediscoverblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/blog-banner.jpg?w=519&h=142)
Thank you for this information.
I see that after Arthur Carriere arrived in Liverpool, he went to S’ cliffe. I am reasonably sure this would have been the primary staging and training area – Shorncliffe, England where most CEF were stationed when arriving in England.
I continue to research and write a book about my grandfather from Winnipeg John Robinson Benson. As Captain JR Benson he was also stationed in Shorncliffe around the same time before being transferred to the Arass area of France.
My book is in the historic fiction genre. JR was known as Rob Benson when he won the Stanley Cup in 1896 with the Winnipeg Victorias. His teammate Rod ‘Roddy’ McLeod Flett from Kildonan was Métis. I have taken creative licence to have them as good friends and Roddy, who is two years older, as a mentor to my grandfather. Flett did not serve during WW I, in fact none of the other 7 teammates served. Roddy was a very successful manager with the CPR who died suddenly playing golf at the Sr Charles Golf Course in 1926.
My grandfather suffered from Shell Shock and left the family (5 children and wife) to become a cook in a lumber camp in northern BC.
I am researching possible Manitoba Métis connections while overseas – Arthur Carriere may be one. Again I may take some creative license due to lack of factual proof.
I am a retired Hospital Director of Spiritual Care and Licensed Counsellor specializing in grief and loss. Faith, ( rosary beads), nature and horses are predominant themes in my grandfather’s coping with shell Shock.
I will continue to look for possible Flett WW I connections. Roddy’s younger brother Magnus played for the Winnipeg Victorias the next few years.
thank you
Rick